vue Router 4源码解析2:url 如何跳转
在上一篇文章我介绍了如何创建路由,下面我们来分析当输入一个 url 时,如何通过路由跳转到对应页面
基础概念介绍
先介绍一下浏览器的 window.location 对象,通过 location 对象能够访问到 url 每个部分的参数

其次要介绍一下 window.history 对象,history 对象能够操作浏览器会话历史,从而实现页面跳转的效果,history 对象有四个核心对象和属性
-
history.pushState(data, title, [, url])方法:向历史记录栈顶添加一条记录- data:
onpopstate事件触发时作为参数传递 - title:页面标题,除了 safari 之外的浏览器都会忽略 title 参数
- url:页面地址
- data:
-
history.replaceState(data, title, [, url])方法:更改当前历史记录 -
history.state属性:存储上述方法的 data 数据 -
history.scrollRestoration属性:自动的(auto)或手动的(manual)恢复浏览器的页面滚动位置但是通过 history 对象实现路由跳转,刷新页面会重新发起请求,如果服务端没有匹配到请求 url 就会产生 404,所以也需要服务端配合改造,设置一个没有匹配默认返回的地址
结合 location 对象和 history 对象,我们具备了获取 url 和跳转 url 的能力,通过这两个能力,下面我们来分析路由跳转的实现原理
路由跳转实现原理
我们在创建路由时,会定义 history 属性,vue-router 有三种方式:createWebHistory 、 createWebHashHistory 和 createMemoryHistory,因为 createWebHistory 是基于基础 history 对象实现,所以我们分析 createWebHistory 的实现原理
createWebHistory
createWebHistory 方法实现主要分为 5 步,我们先看整体方法示意图,再具体介绍每一步实现
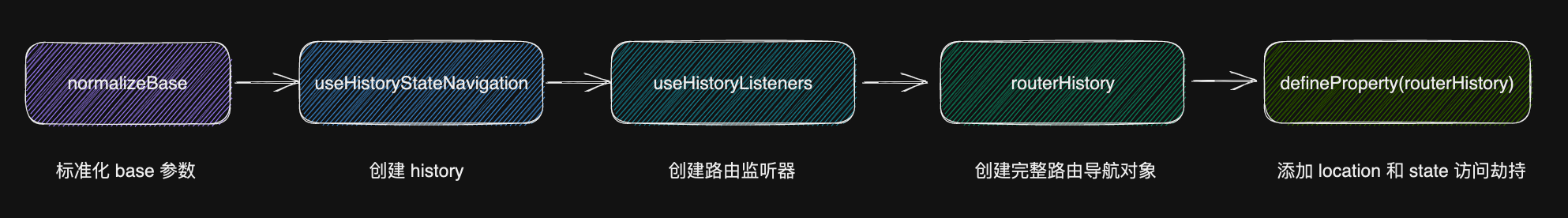
1export function createWebHistory(base?: string): RouterHistory {
2 // 第一步:标准化 base 参数
3 base = normalizeBase(base)
4 // 第二步:创建 history
5 const historyNavigation = useHistoryStateNavigation(base)
6 // 第三步:创建路由监听器
7 const historyListeners = useHistoryListeners(
8 base,
9 historyNavigation.state,
10 historyNavigation.location,
11 historyNavigation.replace
12 )
13 // 第四步:定义 go 方法,创建完成的路由导航对象
14 function go(delta: number, triggerListeners = true) {
15 if (!triggerListeners) historyListeners.pauseListeners()
16 history.go(delta)
17 }
18
19 const routerHistory: RouterHistory = assign(
20 {
21 // it's overridden right after
22 location: '',
23 base,
24 go,
25 createHref: createHref.bind(null, base),
26 },
27
28 historyNavigation,
29 historyListeners
30 )
31
32 // 第五步:添加 location 和 state 访问劫持
33 Object.defineProperty(routerHistory, 'location', {
34 enumerable: true,
35 get: () => historyNavigation.location.value,
36 })
37
38 Object.defineProperty(routerHistory, 'state', {
39 enumerable: true,
40 get: () => historyNavigation.state.value,
41 })
42
43 return routerHistory
44}第一步:标准化 base 参数
通过 normalizeBase 方法处理 base 参数,主要是为了规范化 base 参数,避免错误如果没有传递 base 参数的话,在浏览器环境取 <base> 标签的链接,否则默认为 /,保证 base 前又一个前导斜杠,并移除末尾斜杠
1export function normalizeBase(base?: string): string {
2 // 如果没有传入 base 参数,
3 if (!base) {
4 // 在浏览器中 base 取 <base> 标签的链接,否则默认为 /
5 if (isBrowser) {
6 // respect <base> tag
7 const baseEl = document.querySelector('base')
8 base = (baseEl && baseEl.getAttribute('href')) || '/'
9 // strip full URL origin
10 base = base.replace(/^\w+:\/\/[^\/]+/, '')
11 } else {
12 base = '/'
13 }
14 }
15
16 // 确保 base 前有一个前导斜杠,避免问题
17 if (base[0] !== '/' && base[0] !== '#') base = '/' + base
18
19 // 移除 base 末尾斜杠
20 return removeTrailingSlash(base)
21}第二步:创建 history 对象
通过 useHistoryStateNavigation 方法创建 vue-router 的 history 对象,本质上是对浏览器的 history 对象属性和方法做了一个映射

1function useHistoryStateNavigation(base: string) {
2 const { history, location } = window
3
4 // private variables
5 const currentLocation: ValueContainer<HistoryLocation> = {
6 value: createCurrentLocation(base, location),
7 }
8 const historyState: ValueContainer<StateEntry> = { value: history.state }
9 // 刷新后通过 changeLocation 方法创建 historyState
10 if (!historyState.value) {
11 changeLocation()
12 }
13
14 function changeLocation(): void {}
15
16 function replace(to: HistoryLocation, data?: HistoryState) {}
17
18 function push(to: HistoryLocation, data?: HistoryState) {}
19
20 return {
21 location: currentLocation,
22 state: historyState,
23
24 push,
25 replace,
26 }
27}changeLocation 方法用来更新浏览器历史记录并触发页面导航,首先根据 base 获取跳转的完整 url,在通过 replace 判断通过浏览器的 replaceState 还是 pushState 进行页面跳转
1function changeLocation(
2 to: HistoryLocation,
3 state: StateEntry,
4 replace: boolean
5): void {
6 const hashIndex = base.indexOf('#')
7 // 获取跳转的完整 url
8 const url =
9 hashIndex > -1
10 ? (location.host && document.querySelector('base')
11 ? base
12 : base.slice(hashIndex)) + to
13 : createBaseLocation() + base + to
14 try {
15 // 通过 replace 判断通过 replaceState 还是 pushState 进行页面跳转
16 history[replace ? 'replaceState' : 'pushState'](state, '', url)
17 historyState.value = state
18 } catch (err) {
19 location[replace ? 'replace' : 'assign'](url)
20 }
21}replace 方法和 push 方法都使用到 buildState 创建 state,主要目的是为了在 state 中添加页面滚动位置,在返回到时候能够再回到原来的位置
1function buildState(
2 back: HistoryLocation | null,
3 current: HistoryLocation,
4 forward: HistoryLocation | null,
5 replaced: boolean = false,
6 computeScroll: boolean = false
7): StateEntry {
8 return {
9 back,
10 current,
11 forward,
12 replaced,
13 position: window.history.length,
14 // 记录页面滚动位置
15 scroll: computeScroll ? computeScrollPosition() : null,
16 }
17}replace 方法先通过 buildState 方法创建一个新的 state,再通过 changeLocation 方法进行页面跳转,最后再更新 currentLocation 的值
1function replace(to: HistoryLocation, data?: HistoryState) {
2 const state: StateEntry = assign(
3 {},
4 history.state,
5 buildState(
6 historyState.value.back,
7 // keep back and forward entries but override current position
8 to,
9 historyState.value.forward,
10 true
11 ),
12 data,
13 { position: historyState.value.position }
14 )
15
16 changeLocation(to, state, true)
17 currentLocation.value = to
18}push 方法和 replace 方法类似,但要注意的是,push 方法会通过 changeLocation 进行两次页面跳转,第一次通过 replaceState 进行页面跳转,目的是为了在 state 中记录页面滚动的位置,第二次通过 pushState 才是真正的跳转
1function push(to: HistoryLocation, data?: HistoryState) {
2 const currentState = assign(
3 {},
4 historyState.value,
5 history.state as Partial<StateEntry> | null,
6 {
7 forward: to,
8 scroll: computeScrollPosition(),
9 }
10 )
11
12 // 第一次通过 replaceState 跳转,在 state 记录页面滚动位置
13 changeLocation(currentState.current, currentState, true)
14
15 const state: StateEntry = assign(
16 {},
17 buildState(currentLocation.value, to, null),
18 { position: currentState.position + 1 },
19 data
20 )
21
22 // 第二次通过 pushState 实现 push 跳转
23 changeLocation(to, state, false)
24 currentLocation.value = to
25}第四步:创建路由监听器
通过 useHistoryListeners 方法创建路由监听器,当路由变化时做响应修改,方法主要定义了对于 history 操作事件 popstate 的处理方法 popStateHandler,最后再返回操作监听事件三个方法
1function useHistoryListeners(
2 base: string,
3 historyState: ValueContainer<StateEntry>,
4 currentLocation: ValueContainer<HistoryLocation>,
5 replace: RouterHistory['replace']
6) {
7 // 监听回调函数集合
8 let listeners: NavigationCallback[] = []
9 let teardowns: Array<() => void> = []
10
11 // 暂停状态
12 let pauseState: HistoryLocation | null = null
13
14 // 处理浏览器历史状态更改
15 const popStateHandler: PopStateListener = () => {}
16
17 // 停止监听操作
18 function pauseListeners() {
19 pauseState = currentLocation.value
20 }
21
22 // 添加监听回调函数
23 function listen(callback: NavigationCallback) {}
24
25 // 当用户从当前页面导航离开时记录当前页面滚动位置
26 function beforeUnloadListener() {}
27
28 // 清空 teardowns 数组,移除监听事件
29 function destroy() {}
30
31 // 监听 history 操作事件 popstate
32 window.addEventListener('popstate', popStateHandler)
33 // 监听页面离开的时间 beforeunload
34 window.addEventListener('beforeunload', beforeUnloadListener, {
35 passive: true,
36 })
37
38 return {
39 pauseListeners,
40 listen,
41 destroy,
42 }
43}popStateHandler 方法主要做了两件事
- 处理跳转地址,更新 state 缓存信息,如果是暂停监听状态,停止跳转并重置 pauseState
- 遍历回调函数并执行,相当于发布订阅模式通知所有注册的订阅者
1const popStateHandler: PopStateListener = ({
2 state,
3}: {
4 state: StateEntry | null
5}) => {
6 // 跳转的新地址
7 const to = createCurrentLocation(base, location)
8 // 当前地址
9 const from: HistoryLocation = currentLocation.value
10 // 当前 state
11 const fromState: StateEntry = historyState.value
12 // 计步器,当用户从当前页面导航离开时将调用该函数
13 let delta = 0
14
15 if (state) {
16 currentLocation.value = to
17 historyState.value = state
18
19 // ignore the popstate and reset the pauseState
20 if (pauseState && pauseState === from) {
21 pauseState = null
22 return
23 }
24 delta = fromState ? state.position - fromState.position : 0
25 } else {
26 // 如果没有 state,则执行 replace 回调
27 replace(to)
28 }
29
30 // 遍历回调事件并执行
31 listeners.forEach((listener) => {
32 listener(currentLocation.value, from, {
33 delta,
34 type: NavigationType.pop,
35 direction: delta
36 ? delta > 0
37 ? NavigationDirection.forward
38 : NavigationDirection.back
39 : NavigationDirection.unknown,
40 })
41 })
42}listen 监听方法向 listeners 数组中存储回调函数,并且在内部定义了 teardown 方法用来清除回调函数
1function listen(callback: NavigationCallback) {
2 listeners.push(callback)
3
4 // 如果 listeners 数组包含 callback,则清空 callback
5 const teardown = () => {
6 const index = listeners.indexOf(callback)
7 if (index > -1) listeners.splice(index, 1)
8 }
9
10 teardowns.push(teardown)
11 return teardown
12}beforeUnloadListener 方法用于在离开页面是,判断 history 中是否有历史页面状态数据,如果有的话,就记录当前页面的位置
1function beforeUnloadListener() {
2 const { history } = window
3 if (!history.state) return
4 // 如果 history 中有状态,则通过 scroll 记录当前页面位置
5 history.replaceState(
6 assign({}, history.state, { scroll: computeScrollPosition() }),
7 ''
8 )
9}destory 方法清空 teardowns 数组,移除监听事件
1function destroy() {
2 // 清空 teardowns 数组,移除监听事件
3 for (const teardown of teardowns) teardown()
4 teardowns = []
5 window.removeEventListener('popstate', popStateHandler)
6 window.removeEventListener('beforeunload', beforeUnloadListener)
7}第四步:创建完整路由导航对象
定义 go 方法,可以直接使用计步器跳转到对应历史路由,再将 location、base 等状态合并创建完成的路由导航对象
1// 定义 go 方法,如果第二个参数 triggerListeners 为 false 则暂停监听
2function go(delta: number, triggerListeners = true) {
3 if (!triggerListeners) historyListeners.pauseListeners()
4 history.go(delta)
5 }
6
7 // 创建完整的路由导航对象
8 const routerHistory: RouterHistory = assign(
9 {
10 // it's overridden right after
11 location: '',
12 base,
13 go,
14 createHref: createHref.bind(null, base),
15 },
16
17 historyNavigation,
18 historyListeners
19 )
20}第五步:添加 lacation 和 state 访问劫持
添加 lacation 和 state 访问劫持,保证访问 location 和 value 属性时获取的是具体值而不是代理对象
1// 第五步:添加 lacation 和 state 访问劫持
2Object.defineProperty(routerHistory, 'location', {
3 enumerable: true,
4 get: () => historyNavigation.location.value,
5})
6
7Object.defineProperty(routerHistory, 'state', {
8 enumerable: true,
9 get: () => historyNavigation.state.value,
10})createWebHashHistory
createWebHashHistory 本质也是基于 createWebHistory 的方式来实现,在 base 中会默认拼接一个 #,在回顾下第一幅图,如果 url 链接中带有 # 后面的部分会作为锚点,就不会再刷新时请求服务器。最后再将处理好的 base 参数传入 createWebHistory 方法,同样借助 history 实现路由跳转
1export function createWebHashHistory(base?: string): RouterHistory {
2 base = location.host ? base || location.pathname + location.search : ''
3 // 确保链接会拼接一个 #
4 if (!base.includes('#')) base += '#'
5
6 return createWebHistory(base)
7}createMemoryHistory
createMemoryHistory 方法用于服务端渲染,因为服务端没有浏览器的 history 对象,所以实现方式是基于内存,下面我们简单分析一下具体实现
在 createMemoryHistory 方法中,定义 queue 作为历史记录的存储队列,定义 position 作为计步器,设置 location、push、replace 的方法都是基于 queue 的出队入队操作实现,最后再将相关路由操作方法放在 routerHistory 对象中返回
1export function createMemoryHistory(base: string = ''): RouterHistory {
2 let listeners: NavigationCallback[] = []
3 let queue: HistoryLocation[] = [START]
4 let position: number = 0
5 // 第一步:
6 base = normalizeBase(base)
7
8 function setLocation(location: HistoryLocation) {
9 position++
10 if (position === queue.length) {
11 // we are at the end, we can simply append a new entry
12 queue.push(location)
13 } else {
14 // we are in the middle, we remove everything from here in the queue
15 queue.splice(position)
16 queue.push(location)
17 }
18 }
19
20 // 触发监听回调函数执行
21 function triggerListeners(
22 to: HistoryLocation,
23 from: HistoryLocation,
24 { direction, delta }: Pick<NavigationInformation, 'direction' | 'delta'>
25 ): void {
26 const info: NavigationInformation = {
27 direction,
28 delta,
29 type: NavigationType.pop,
30 }
31 for (const callback of listeners) {
32 callback(to, from, info)
33 }
34 }
35
36 const routerHistory: RouterHistory = {
37 // rewritten by Object.defineProperty
38 location: START,
39 // TODO: should be kept in queue
40 state: {},
41 base,
42 createHref: createHref.bind(null, base),
43
44 replace(to) {
45 // remove current entry and decrement position
46 queue.splice(position--, 1)
47 setLocation(to)
48 },
49
50 push(to, data?: HistoryState) {
51 setLocation(to)
52 },
53
54 listen(callback) {
55 listeners.push(callback)
56 return () => {
57 const index = listeners.indexOf(callback)
58 if (index > -1) listeners.splice(index, 1)
59 }
60 },
61 destroy() {
62 listeners = []
63 queue = [START]
64 position = 0
65 },
66
67 go(delta, shouldTrigger = true) {
68 const from = this.location
69 const direction: NavigationDirection =
70 delta < 0 ? NavigationDirection.back : NavigationDirection.forward
71 position = Math.max(0, Math.min(position + delta, queue.length - 1))
72 if (shouldTrigger) {
73 triggerListeners(this.location, from, {
74 direction,
75 delta,
76 })
77 }
78 },
79 }
80
81 Object.defineProperty(routerHistory, 'location', {
82 enumerable: true,
83 get: () => queue[position],
84 })
85
86 return routerHistory
87}